Table Of Content
From small, three-story buildings to massive high-rises, scaffolding is used for a wide variety of construction, inspection, maintenance and repair projects. According to OSHA, 65 percent of the construction industry, an estimated 2.3 million construction workers, work on scaffolding frequently. Employees who assemble and remove scaffolds must be trained by a trainer with knowledge and experience and supervised by a competent person. Not only does the competent person need to know how to erect, move, inspect and maintain the scaffold, he needs to make sure that employees are working safely while on the scaffold. This person should be identified on company letterhead for each site, along with his qualifications and authority to correct hazards.
What Is Scaffolding?
In addition, scaffolding is consistently among the top 10 most frequently cited OSHA standards violations. Employees shall be prohibited from working on scaffolds covered with snow, ice, or other slippery material except as necessary for removal of such materials. Scaffold components manufactured by different manufacturers shall not be intermixed unless the components fit together without force and the scaffold's structural integrity is maintained by the user. Off-Highway Research offers a library of more than 200 regularly updated reports, providing forensic detail on key aspects of the construction equipment industry. The web pages currently in English on the EDD website are the official and accurate source for the program information and services the EDD provides.
Vision and OSHA Top 10 Violations
"Large area scaffold" means a pole scaffold, tube and coupler scaffold, systems scaffold, or fabricated frame scaffold erected over substantially the entire work area. The disappointing reality in the scaffold industry is that too often training is offered by those who have marginal qualifications to do so. Since there is no licensing program that verifies the instructor is qualified, be sure to carefully choose your instructor. Forms and publications provided on the EDD website cannot be translated using Google™ Translate. High school students use Guides to identify attractive careers and focus their education and training plans to meet job entrance requirements. (3) – Where inadequacies in an affected employee’s work involving scaffolds indicate that the employee has not retained the requisite proficiency.
How Drones Can Reduce the Need for Internal Scaffolding in Inspection Work
The Circle Safety & Health Consultants Competent User/Inspector Course will fulfill OSHA scaffolding requirements for competent person training. The highly knowledgeable staff at Circle Safety will provide comprehensive training and valuable content materials. Interestingly, the parameters governing the design and construction of scaffolds has defaulted to the U.S. It’s a dangerous assumption since the one regulation that is consistently ignored is the one that requires a scaffold to be designed by a qualified person.
Scaffold collapses prompt warning - SafeWork SA
Scaffold collapses prompt warning.
Posted: Wed, 13 Mar 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
OSHA says a competent person must also have the authority to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate such hazards. Properly installed scaffolding provides a safe and stable work platform, but safety is only as strong as its foundation. Scaffold construction requires strict standards, frequent inspections, and daily maintenance to ensure proper and safe use. The federal government lists scaffolding safety as one of the most commonly cited workplace violations.
General Requirements
In addition to workers’ comp and time lost due to job site shutdowns, a poor safety record could negatively impact landing future jobs. Fulfilling OSHA’s competent person requirement helps prevent those costs and ensures worker safety. In addition to a fine or citation from OSHA, not having a competent person inspector can lead to the entire job getting shut down due to workers not being able (or willing) to use an unsafe scaffold. Trestle scaffolding is usually used in small spaces for painting or minor repairs.
For adjustable suspension scaffolds, this can apply with the scaffold operating at either the rated load of the hoist, or two times minimum the stall load of the hoist, again whichever is greater. Workers can be exposed to many hazards when working around scaffolding, including falls from elevation, due to the lack of fall protection. Employees can be struck by falling tools, work materials, or debris, or they can be potentially electrocuted due to the proximity of the scaffolding to the overhead power lines.
If the scaffolding is long or needs to support a lot of weight, workers may need to add additional support to its base. Double scaffolding uses a two-tier support to ensure stability, with additional support provided by cross braces and rakers. This type of scaffold can get rid of the need for unsightly frames or poles to be used on the fronts of buildings, and is often constructed near balconies to give workers an easy way to access it. Inspections are typically the first step in a maintenance process, since they uncover areas that may require maintenance.
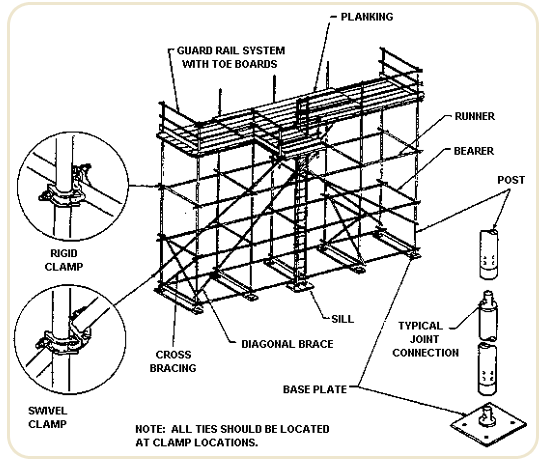
In general, each scaffold and scaffold component shall be capable of supporting, without failure, its own weight and at least 4 times the maximum intended load applied or transmitted to it. Scaffolds shall be designed by a qualified person and shall be constructed and loaded in accordance with that design. Employers must make sure that workers are not allowed to work on scaffolds covered with snow, ice, or other slippery material except as necessary to remove such materials. Work on or from scaffolds is also not allowed during storms or high winds unless a competent person has determined that it is safe for workers to be on the scaffold and those workers are protected by a personal fall arrest system or wind screens. Wind screens are not to be used unless the scaffold is secured against the anticipated wind forces. (d)(3)(i) – Before the scaffold is used, direct connections shall be evaluated by a competent person who shall confirm, based on the evaluation, that the supporting surfaces are capable of supporting the loads to be imposed.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover essential scaffold safety practices, including scaffold plank inspection, fall protection, and worker training, ensuring that your construction site remains accident-free and conducive to a productive work environment. Understanding these safety measures will not only help protect your team but also contribute to a more efficient construction process, minimizing downtime and promoting smooth project execution. However, ladder jack scaffold, top plate bracket scaffold roof bracket scaffold, and pump jack scaffold shall be at least 12 inches wide.
A scaffold, also called scaffolding or staging, is a temporary structure that allows people to stand on a stable platform for work at height or in hard-to-reach places. In the modern age, scaffolding has developed far beyond these early versions, and now comes in several different designs made from several different types of materials. Scaffold planks are a critical component of the overall scaffold system, and regular inspection and maintenance are vital for ensuring structural integrity and worker safety. In terms of the type of work being performed, tubular welded frame scaffolding is well-suited for most construction projects due to its easier assembly and disassembly. In industrial settings with piping and obstructions, modular scaffolding generally works better because it can be configured around obstacles and unusual shapes more easily than tubular welded frame scaffolding.
There are no standards or putlogs, only working platforms supported by movable ladders. Single scaffolding is one of the oldest construction methods, and it’s commonly used for work on brick masonry. Though relatively simple, this approach creates a sturdy and reliable structure for work at height. Patented scaffolds are readymade and have special couplings and frames attached, coming with brackets that support the working platform. In some types, the brackets can be adjusted to different levels to support work at various heights.
To this day, scaffolding remains one of the most useful and efficient ways for people to work at height. Peoples as diverse as Nubians, Egyptians, and Chinese have documented the use of scaffolding for constructing tall buildings, using rudimentary scaffolds made of wood and tied at the top with ropes. Incidents involving scaffolding account for 4,500 workplace injuries and 50 deaths per year.
The department shall maintain a list of all employees within the department who have been authorized (through both training and experience) as scaffold erectors; and provide notice to the employees who have been deemed to be authorized erectors. Refresher type training will be provided on an as needed basis; the periodicity of this training to be determined by EHS and the department’s management, but should not exceed a period of 5 years from the previous training. The employer provides safe means of access for each employee erecting or dismantling a scaffold where the provision of safe access is feasible and does not create a greater hazard. The employer has a competent person determine whether safe access is feasible or would pose a greater hazard to provide and have employees use a safe means of access.
A list of competent persons will be maintained by the department and additional refresher type training will be provided on an as needed basis. The periodicity of this training to be determined by EHS and the department’s management, but should not exceed a period of 5 years from the previous training. The department also to provide competent person with document indicating that they are competent persons representing their respective departments and shall agree to uphold all local, state, and federal rules and regulations as they relate to scaffolding.